The Mole & Avogadro Constant
-
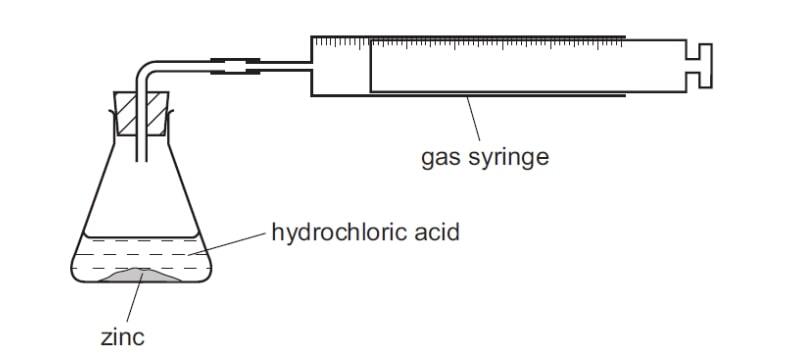
Reaction setup and gas collection (context) Context: A student investigated the reaction of zinc powder with dilute hydrochloric acid using a gas-syringe setup. The same mass of zinc was added to different volumes of acid at 20°C (room temperature). For each experiment, the total volume of hydrogen gas produced was measured.
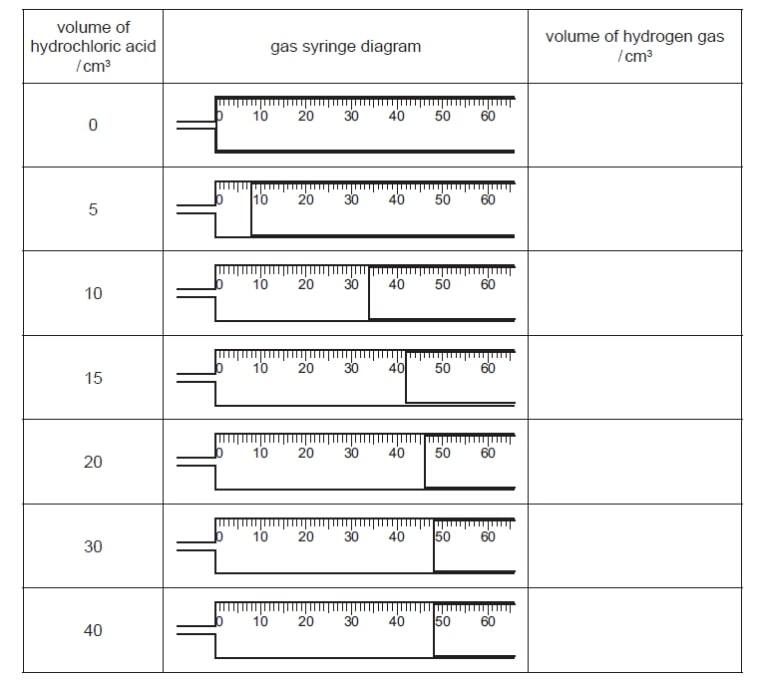
Apparatus for zinc + dilute hydrochloric acid (a) Use the gas syringe diagrams to record the volumes of hydrogen gas in the table.
HCl volume (cm³) H₂ collected (cm³) (b) On the grid, plot the points and draw a smooth line graph.
(c)
(d) Explain why the volume of hydrogen gas does not increase after 30 cm³ of hydrochloric acid.
(e) Sketch on the grid the graph you would expect if the experiments were repeated using the same mass of zinc granules.
-
Calcium burns in air to form calcium oxide. The reaction is vigorous and some of the calcium oxide can be lost as smoke.
Plan an investigation to determine the maximum mass of oxygen that combines to form calcium oxide when 2 g of calcium granules are burnt in air.
You are provided with common laboratory apparatus and calcium granules.
-
Some documents are stored in containers with packets of silica gel crystals. These crystals absorb water from air that enters the container. Water could damage the documents. Anhydrous cobalt(II) chloride is added to the silica gel. As the crystals absorb water they change colour from blue to pink. Heating the silica gel in an oven removes the water from the crystals so that the crystals can be reused.
Plan an experiment to find the mass of water absorbed by a packet of silica gel crystals.